The Industry 4.0 framework has induced change in manufacturing by enabling automation to digitalize the entire value chain – from plant management to plant operations. It has connected the physical and digital worlds and facilitated the convergence of Operational Technology (OT) with Information Technology (IT).
OT covers industrial control systems, industrial control management framework, and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition Systems. In contrast, IT focuses on confidentiality and availability of hardware, software, networks, cloud, storage, data, servers, endpoints, and systems. The conjunction of OT and IT has resulted in increased adoption of robotics, digital twins, and automated systems and processes.
The union has ensured real-time asset and process monitoring, proactive and predictive maintenance, closed-looped data models, IoT-enabled quality improvement initiatives, and customization of products.
Data from connected assets are collected into a data lake and used by advanced AI-Ml-driven big data analytics to transform existing manufacturing processes, predict machine failures and maximize production efficiencies. The data is collected from cloud, and industrial IoT (IIoT) platforms using smart sensors.
Digital transformation by leveraging IIoT devices to integrate industrial control systems with systems, processes, and analytics has irrefutable advantages. It streamlines efficiencies of industrial ecosystems, making them more effective and easier to operate. Uptime is improved by constant monitoring of system performance through predictive maintenance to reduce repairs and enhance productivity.
Though the integration of OT and IT is of strategic importance, it is vulnerable to attacks. Previously siloed OT systems are now connected to the internet through IoT devices, exposing them to threats such as ransomware and DDoS attacks. Moreover, the remote access of these systems has also expanded the attack surface. Some critical security challenges include lack of data security, weak user authentication practices, limited visibility, patching OT systems, reactive security approaches, remote maintenance, managing different OT environments, absence of incident management and response plans, non-existence of automated AI-driven breach prevention, and inadequate security awareness.
Manufacturing infrastructure is of critical national importance for any economy. OT & IT networks and processes must enhance security resilience to mitigate the risks from intelligent cyber intrusions.
The IBM X-Force, Threat Intelligence Report Index 2020 findings show a staggering 2000% rise in OT infrastructure related cyber incidents. Commonly faced threats include software vulnerabilities that allow attackers to manipulate licenses, execute remote code, or deny services. It can also be stealth malware for remote administration of attacks or large-scale complex attacks targetting multiple operating systems.
These incidents can be proactively mitigated and minimized. A risk-based security approach can enable 24×7 monitoring to ensure device and asset visibility across OT networks, restrict access to devices and applications, network and wireless traffic monitoring, and role-based controls through identity and access management.
The first step in this approach is to devise a comprehensive OT security strategy by understanding the security risks. This is needed as OT security risks in manufacturing are essentially different and integrity of processes and systems availability are of paramount importance to sustain production levels.
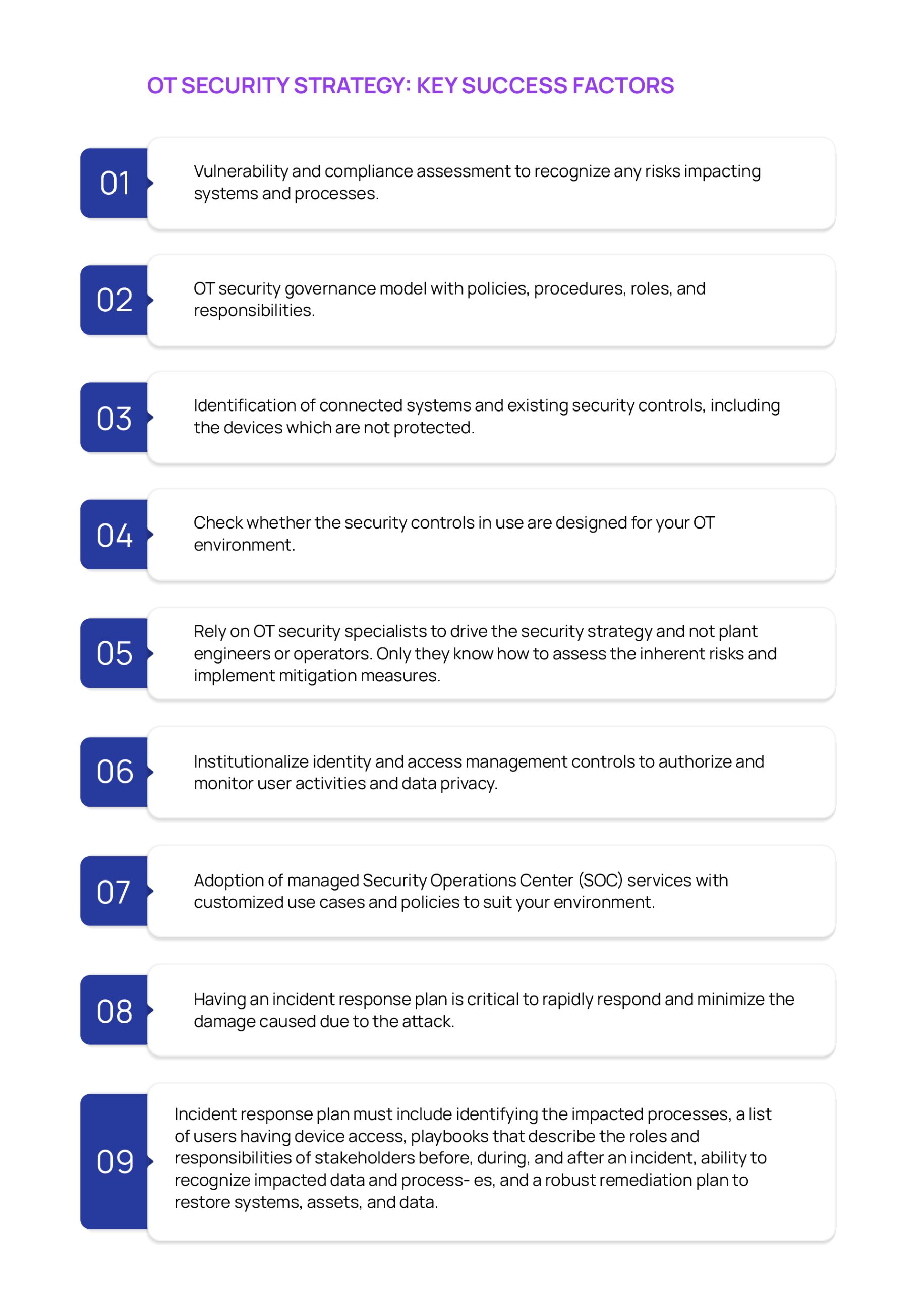
Digitization in manufacturing is hastening the use of IoT devices, resulting in the emergence of smart factories that are connected, responsive, and adaptive. The burgeoning use of devices can present an enterprise security risk, with attackers targeting OT environments having IIoT equipment for malicious use. Its time for an asset-intensive industry such as manufacturing to be wary of cyber threats, develop in-depth visibility to the OT threat landscape and deploy highly available secure operations to enhance security maturity.






